So, you want to build a successful startup but are unsure where to begin. You’ve heard about the “lean startup methodology,” but what does that approach mean? Let’s cover the attributes of a successful lean startup so you can apply them to your own business idea.
Prepare yourself as we discuss the details of how lean startups succeed. Success goes beyond great concepts and sharp pitches—it is rooted in adopting certain critical attributes of successful lean startup practices right from the start.
Table Of Contents:
- Attributes of a Successful Lean Startup
- Minimum Viable Product (MVP)
- Validated Learning
- Build-Measure-Learn Feedback Loop
- Agile Development Cycles
- Business Model Canvas
- Customer Feedback Integration
- Reducing Wasteful Practices
- Adapting to Market Demand
- Core Principles of Lean Startups
- Conclusion
Key Attributes of a Successful Lean Startup
In today’s fast-paced business world, the lean startup methodology has become a game-changer for entrepreneurs looking to build successful ventures. By focusing on key attributes like rapid experimentation, validated learning, and continuous improvement, lean startups can navigate the challenges of launching and scaling a business with greater agility and efficiency.
Statistics indicate that about seventy-five percent of startups fail. Yet, embracing core principles from the lean startup method can help entrepreneurs tilt the scales in their favor. Inspired by Eric Ries’s insights in “The Lean Startup,” this framework transforms product creation and customer acquisition strategies for many emerging companies.
One of the defining characteristics of a lean startup approach is its emphasis on creating a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) and iterating based on customer feedback. By quickly bringing a basic version of their product to market, lean startups can validate their assumptions, gather valuable insights, and make data-driven decisions to refine their offering.
Minimum Viable Product (MVP)
At the heart of the lean startup methodology lies the concept of Minimum Viable Product (MVP). An MVP is a stripped-down product with only the essential features needed to test the market and gather customer feedback. By focusing on creating an MVP, lean startups can reduce risks, minimize waste, and align their efforts with the needs and preferences of their target audience.
Benefits of Minimum Viable Product (MVP)
Developing an MVP offers numerous benefits for lean startups. First and foremost, it allows entrepreneurs to test their business model and value proposition quickly and cost-effectively. Rather than investing significant resources into building a fully-featured product, lean startups can use an MVP to validate their hypotheses and gather real-world data on customer behavior and preferences.
Moreover, by launching an MVP, lean startups can generate revenue and build brand awareness early. This helps offset development costs and provides valuable insights into pricing strategies, marketing channels, and customer acquisition tactics. With an MVP in the market, lean startups can continuously iterate and improve their product based on user feedback, ensuring they always deliver value to their customers.
Validated Learning
A big reason why lean startups succeed is their focus on validated learning. They don’t just go with hunches; they gather real-world data and listen closely to customers before deciding anything. This constant cycle of testing ideas helps them figure out the best path forward faster than others who stick with unproven assumptions.
The backbone of lean product development lies in collecting solid user feedback via techniques such as A/B testing or engaging directly through interviews while observing how they interact analytically. Armed then equipped thoroughly –they’ll be ready when it comes time to decide upon impactful aspects from new additions all the way down, even tweaking old ones and adjusting rates so everything aligns seamlessly precisely matching up just right with every current prevailing trend demand happening around out there today
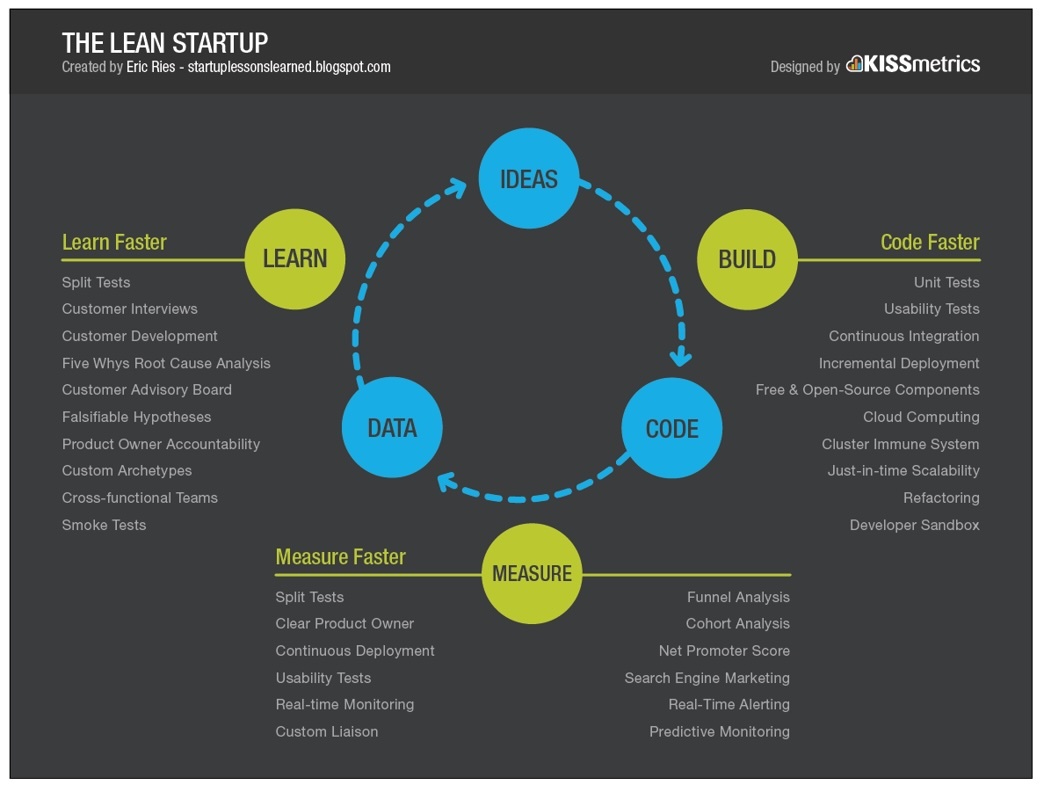
Build-Measure-Learn Feedback Loop
At the core of the lean startup methodology is the Build-Measure-Learn feedback loop. This iterative process involves rapidly building a product or feature (Build), measuring its performance, gathering data (Measure), and then using those insights to inform future development decisions (Learn). By continuously cycling through this loop, lean startups can refine their offerings based on real-world data and user feedback.
In markets driven by swift changes in customer preferences or fast-moving tech advancements, leaning into the Build-Measure-Learn process helps keep things fresh. It enables lean startups to test ideas quickly and refine them based on real-time data, ensuring they don’t fall behind but rather set new trends.
Agile Development Cycles
Lean startups rely heavily on agile development cycles to bring their products to market quickly and efficiently. Unlike traditional businesses that often follow a linear, waterfall approach to product development, lean startups embrace a more flexible and iterative process. By breaking down their development efforts into smaller, manageable sprints, lean startups can rapidly prototype, test, and refine their offerings based on real-time feedback.
This agile approach allows lean startup processes to adapt swiftly to changing market conditions and customer needs. By prioritizing speed and flexibility over perfection, lean startups can get their products into users’ hands faster, gathering valuable insights and making data-driven improvements. This iterative process reduces the risk of building the wrong product, like traditional startups, and enables lean startups to continuously deliver value to their customers.
Business Model Canvas
Another essential tool in the lean startup toolkit is the Business Model Canvas. This strategic management template helps entrepreneurs visualize and develop their business models by breaking down key components such as customer segments, value propositions, revenue streams, and cost structures. By using the Business Model Canvas, lean startups can quickly iterate on their business model and identify areas for improvement.
For lean startups, the Business Model Canvas focuses on customer needs in product development. It guides entrepreneurs in aligning offerings with target audience preferences, ensuring they create something valuable rather than useless clutter no one will buy.
Customer Feedback Integration
Successful lean startup principles understand the importance of integrating customer feedback into their product development process. By actively seeking out and listening to user input, lean startups can continuously improve their offerings and deliver greater value to their customers. This feedback loop is essential for building products that solve real problems, delight users, and foster long-term loyalty.
Lean startup approaches employ various techniques, such as user interviews, surveys, and usability testing, to integrate customer feedback effectively. Entrepreneurs can gain valuable insights into customer pain points, preferences, and behavior by engaging directly with their target audience. This information can then inform product roadmaps, prioritize features, and optimize the user experience for market success.
Reducing Wasteful Practices
One key principle of the lean startup methodology is eliminating wasteful practices. By focusing on activities that deliver real value to customers and cutting out unnecessary overhead, lean startups can maximize their efficiency and resource utilization. This approach helps reduce costs and enables lean startups to move faster and adapt quickly to changing market conditions.
To spot and eliminate waste, lean startups use tools like value stream mapping and constant process tweaking. Entrepreneurs look at where things are getting stuck or slowing down so they can focus more on what matters—growing the business profitably without pouring money into extras nobody needs.
Adapting to Market Demand
Successful lean startups are highly attuned to market demand and can quickly pivot based on changing customer needs and preferences. By continuously monitoring market signals and gathering user feedback, lean startups can identify emerging trends, anticipate shifts in consumer behavior, and adapt their offerings accordingly. This agility is essential for staying relevant and competitive in today’s fast-paced business environment.
To effectively adapt to market demand, lean startups often employ market segmentation, customer development, and rapid experimentation techniques. By deeply understanding their target audience and testing new ideas quickly, entrepreneurs can validate their assumptions and make data-driven decisions about product development and go-to-market strategies. This approach helps lean startups avoid the common pitfall of building products out of sync with market needs.
Core Principles of Lean Startups
In the lean startup world, core ideas like continuous learning from real data, continuous improvement of processes, and being ready to change direction if needed are crucial. Entrepreneurs who adhere to these attributes of a successful lean startup can better handle market uncertainties.
Other key principles of lean startups include a bias towards action, a focus on customer value, and a commitment to experimentation and iteration. By prioritizing speed and learning over perfection, lean startups can quickly test their assumptions, gather valuable insights, and make data-driven decisions to refine their offerings. This approach reduces the risk of failure and enables lean startups to continuously deliver value to their customers and stay ahead of the competition. 7 Key Attributes of a Successful Lean Startup
Conclusion
Building a successful startup is no easy feat, but by focusing on these seven key attributes of a successful lean startup, you’ll be well on your way.
Remember, it’s all about creating a minimum viable product, validating your assumptions through customer feedback, and being willing to pivot when necessary. Embrace agile development, keep your business model flexible, and always be learning.
The path of a lean startup is full of twists and turns, but with the right mindset and approach, you can navigate the challenges and come out on top. So go forth, intrepid entrepreneur, and make your mark on the world!
Subscribe to my LEAN 360 newsletter to learn more about startup insights.