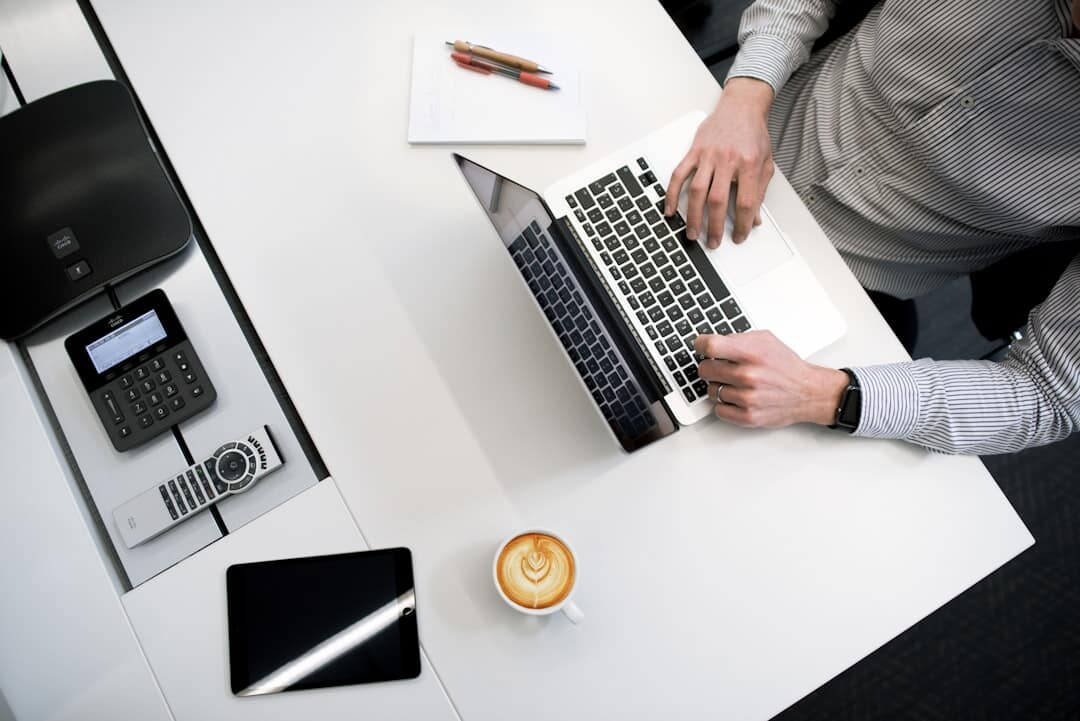
Are you exploring ways to generate income without trading every single hour for a dollar? Many founders and investors eventually look into acquiring existing assets that can produce cash flow more automatically. Finding the best business to buy for passive income is a frequent goal, but understanding what ‘passive’ means is important.
It seldom involves doing absolutely nothing. Certain businesses, however, require significantly less active management than others once set up properly, helping you earn passive income.
Buying a business to build wealth over time is a logical step for many business owners. Instead of starting from scratch, you acquire something already operational, possibly with an existing customer base. The aim is to find a setup where systems, processes, or existing management allows earnings without constant direct involvement, letting you generate passive income.
Table of Contents:
- Understanding Passive Income Businesses
- Top Contenders for the Best Business to Buy for Passive Income
- Factors to Consider Before Buying
- Conclusion
Understanding Passive Income Businesses
What characterizes a business as potentially ‘passive’? Generally, it means the business can operate and generate revenue without your constant, hands-on involvement day to day. This could be because the business model is largely automated or relies on dependable managers or systems.
Consider businesses where the primary asset performs the main function, like machines, property, or digital products used for selling products online. This doesn’t eliminate work, particularly during the initial setup or acquisition phase. It simply means the ongoing operational demand on you, the owner, can be substantially reduced, freeing up time compared to managing active income sources.
Exploring different passive income ideas can reveal opportunities beyond traditional employment. People starting out might consider simpler options before committing to buying a full business. However, acquiring an established passive income business can accelerate wealth generation.
What “Passive” Really Means
Purely passive income from a business you actively own is quite rare. Some oversight, financial review, strategic decision-making, or management of managers will always be necessary. Passive income is typically defined as earnings from a rental property, limited partnership, or another venture where a person isn’t actively involved daily.
The emphasis is on ‘not actively involved’ in routine operations. Your function changes from operator to owner or supervisor. Instead of dedicating 40+ hours weekly to running the business, you might spend a few hours weekly or monthly on reviews and strategy, aiming to achieve a steady stream of income.
This shift is the primary objective for most individuals seeking passive income businesses as a primary income source or supplementary extra money. It contrasts sharply with the demands of active income generation. Passive investors often look for opportunities requiring minimal time commitment.
Top Contenders for the Best Business to Buy for Passive Income
Let’s examine specific business types frequently discussed regarding passive income potential. The degree of passivity greatly depends on the particular business’s structure and management. Conducting thorough due diligence is essential before any purchase.
Remember, the goal is to find a business running smoothly with minimal input. Different models suit different financial situations and risk tolerances. Considering alternatives like real estate investments or even simpler methods like high-yield savings accounts can provide context.
Laundromats
Coin-operated laundromats represent a traditional example. The machines handle the core task of washing and drying clothes. Customers usually operate the equipment themselves.
Primary owner responsibilities include collecting revenue, maintaining machines, ensuring cleanliness, and addressing occasional customer problems. Many owners employ attendants or maintenance personnel, further reducing direct involvement. Incorporating modern payment systems can also streamline operations.
The initial investment can be considerable due to commercial real estate and equipment costs. However, a strategically located and well-kept laundromat can yield steady cash flow. Location relative to local communities and competition level are critical factors.
Self-Storage Facilities
Similar to laundromats, self-storage facilities utilize physical assets – the storage units – to generate income. Customers rent space on a monthly basis, and management can often be significantly automated.
Features like online booking, automated billing systems, and electronic gate access minimize the need for continuous on-site staffing. Oversight is still required for security, maintenance, and handling less frequent customer service issues. Hiring a part-time manager or engaging a third-party property manager are common strategies.
The investment needed is substantial, especially for acquiring or constructing a facility. Key performance metrics include occupancy rates and local market demand analysis. The self-storage sector has demonstrated consistent growth, indicating stability, making it a potentially great passive income source.
Car Washes
Automated car washes, particularly in-bay automatic or tunnel systems, can be effective passive income businesses. The machinery performs the service, and payment collection is frequently automated.
Owner involvement typically centers on maintenance schedules, supply management, marketing efforts, and financial supervision. Similar to laundromats, maintaining functional equipment is crucial for uninterrupted cash flow. High visibility and accessible location are essential for attracting clientele.
Various models exist, ranging from basic coin-operated bays to advanced tunnel washes. Greater automation usually leads to increased passivity, although this often correlates with higher initial investment and more complex maintenance needs. Employing staff for cleaning and basic upkeep can further decrease your direct operational tasks.
Vending Machine Routes
Owning a route of vending machines situated in diverse locations can generate passive income effectively. The machines automate the process of selling products.
The primary ‘work’ involves restocking machines, collecting payments (cash and increasingly cashless via modern payment options), and maintaining the equipment. While managing this yourself can be time-consuming, hiring someone to oversee route operations is a viable option for this vending machine business. Identifying profitable locations and ensuring machine reliability are keys to success.
Scalability is an important consideration; a small route might not produce significant income. Expanding the route or utilizing technology for inventory management can enhance efficiency and profitability. Profit margins are heavily influenced by product costs and the sales volume per machine business.
Established Content Websites or Blogs
Acquiring an existing website or blog that earns revenue through advertising, affiliate marketing, or digital product sales can be a relatively passive income business. If the site possesses strong search engine rankings and maintains a consistent flow of traffic, it can generate money with less direct effort. This represents one type of many successful online businesses.
Ongoing tasks include updating content, managing SEO strategies, and potentially overseeing partnerships or product updates. Much of this work, including creating content, can be outsourced to writers, editors, virtual assistants, or content creators. Your role would involve overseeing the overall strategy and monitoring performance metrics, possibly using social media platforms for promotion.
Thorough due diligence is vital in this area. It’s necessary to verify traffic sources (like social media), revenue statements, and the website’s reputation with search engines such as Google. Websites heavily dependent on a single traffic source or income stream carry higher risks. Consider if the site focuses on a small niche or broader topics.
Automated E-commerce Stores
Consider e-commerce businesses utilizing models like dropshipping or Amazon FBA (Fulfillment by Amazon). In these frameworks, order fulfillment and sometimes customer service tasks are managed by third parties.
With dropshipping, you avoid holding inventory; suppliers ship products directly to your customers. Using Amazon FBA, Amazon stores your inventory and handles the shipping and returns processes. Your focus shifts mainly to marketing, product selection, and managing relationships with suppliers or optimizing Amazon listings.
These online businesses are not entirely hands-off, as marketing activities and platform management require ongoing effort. However, the operational burden is significantly less compared to traditional retail models. Selling products through these channels requires understanding online marketing and platform rules.
Small SaaS Businesses
Software as a Service (SaaS) businesses offering subscription-based software products can become passive income sources, especially if the product is mature and stable. Revenue is generated from recurring monthly or annual subscriptions, providing a steady stream of income.
If the software needs minimal ongoing development and customer support is efficient or manageable by a small team, your oversight role could be limited. This model often performs well for software addressing a specific, ongoing need within a small niche market. Some successful online ventures are SaaS based.
Acquiring a SaaS business generally requires some technical understanding or access to technical expertise for maintenance and future updates. Customer churn rate (the rate at which customers cancel subscriptions) is a critical metric to monitor closely. Valuations for SaaS businesses can be high due to the attractive recurring revenue model, but they can be a good option for passive investors.
Real Estate Investments (Rental Property)
Buying rental property is a well-known path toward generating passive income through rental income. Whether it’s single-family homes, multi-family units, or commercial buildings, owning real estate can provide consistent cash flow. This type of real estate investment requires capital but can build significant wealth over time.
Management involves finding tenants, collecting rent, handling maintenance, and managing finances. Many passive investors hire a property manager to handle these daily tasks, making it a more hands-off rental business. The level of passivity depends heavily on whether you self-manage or delegate.
Location, property condition, and financing significantly impact returns. Real estate investments require understanding local markets and property valuation. While potentially lucrative, it involves significant capital and carries market risks.
Parking Lots or Spaces
Owning a parking lot or even a single private parking space in a high-demand area can be a surprisingly effective passive income source. This could range from a small parking lot near a busy venue to leasing out a private parking space in a dense urban area. The initial investment varies greatly depending on location and size.
Management can be minimal, especially for smaller operations. Automated payment systems (using modern payment technology or a mobile app) and basic maintenance (cleaning, signage) are the main tasks. For larger lots, hiring an attendant or using a management company might be necessary.
Demand is highly location-dependent. Researching traffic patterns, local events, and competition in local communities is crucial. This income business model offers simplicity and potentially low operating costs, making it a good option for some passive investors.
Other Passive Income Ideas to Consider
Beyond buying entire businesses, other avenues exist for making money with less active effort. Creating and selling online courses allows you to leverage your expertise; once created, the course can generate sales over time with primarily marketing efforts. Developing a popular YouTube channel takes significant work upfront creating content, but successful channels earn through ads and sponsorships with ongoing, yet often flexible, effort.
Investing options like building a bond ladder or investing in bond funds can provide a steady stream of income with relatively low effort compared to running a business. Peer-to-peer lending platforms allow individuals to lend money to others and earn interest, though this carries credit risk. Even high-yield savings accounts offer a very low-risk way to earn some passive income, though returns are typically modest compared to business ownership or other investments.
Affiliate marketing, often combined with a content website or social media presence, involves earning commissions by promoting other companies’ products. While requiring content creation and audience building, it avoids the complexities of product development or inventory management. Evaluating these various income ideas can help determine the best fit for your financial situation and desired time commitment.
| Business Type | Typical Upfront Cost | Potential Passivity Level | Common Tasks | Key Success Factors |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Laundromat | High | Medium to High (with staff) | Collections, Maintenance, Cleaning | Location, Equipment Reliability |
| Self-Storage | Very High | High (with automation/manager) | Security, Maintenance, Billing | Location, Occupancy Rates |
| Car Wash (Automated) | High | Medium to High | Maintenance, Supplies, Marketing | Location, Equipment Uptime |
| Vending Machine Route | Low to Medium | Medium (High if self-managed) | Stocking, Collections, Repairs | Location Profitability, Scale |
| Content Website/Blog | Low to High (acquisition cost) | Medium to High (with outsourcing) | Content Updates, SEO, Marketing | Traffic Quality, Monetization |
| E-commerce (Dropship/FBA) | Low to Medium | Medium | Marketing, Product Selection, Listings | Marketing Skill, Niche Selection |
| SaaS Business | Medium to Very High | Medium to High | Oversight, Minor Updates, Support Mgt. | Low Churn, Product Stability |
| Rental Property | High to Very High | Medium to High (with property manager) | Tenant Mgt., Maintenance, Rent Collection | Location, Tenant Quality, Financing |
| Parking Lot/Space | Low to Very High | High (with automation) | Payment Systems, Basic Maintenance | Location Demand, Pricing |
Factors to Consider Before Buying
Selecting the appropriate passive income business involves more than just choosing from a list. You must evaluate your available capital, existing skills, risk tolerance, and desired time commitment. Understand your own financial situation before proceeding.
Think honestly about the level of involvement you are genuinely prepared for. Some ‘passive’ businesses might still require 5-10 hours per week, while others could be closer to 5-10 hours per month once stabilized. Align your expectations with the reality of the specific business model and your willingness to perform the work upfront.
Consider how you will fund the purchase. Will you use savings, financing, or perhaps funds freed up by using balance transfer credit cards strategically? Understanding the financial implications is paramount before buying any selling business.
Due Diligence is Crucial
Never bypass comprehensive due diligence. This involves a thorough investigation into the business’s financial records, operational procedures, customer base analysis, and legal compliance. Verify all income statements and gain a clear understanding of all associated expenses.
Search for potential hidden issues or critical dependencies. Does the business rely heavily on one key employee, supplier, or customer? What are the prevailing industry trends? Engaging professional advisors, such as accountants and lawyers specializing in business acquisitions, is strongly recommended for making informed decisions.
Failure to conduct proper due diligence is one of the biggest risks when buying a business, potentially leading to unexpected costs or lower-than-expected cash flow. Examine everything from contracts to equipment condition to online reviews. A thorough check provides a realistic picture of the investment.
Your Role Post-Purchase
Define clearly what your responsibilities will be after acquiring the business. Even relatively passive businesses need owner oversight. You will likely monitor key performance indicators (KPIs), review financial reports regularly, make strategic choices, and manage any employees or key contractors.
Evaluate if you need to implement new systems, technology (like a mobile app for customer interaction or payment), or hire additional personnel to increase the business’s passivity beyond its current state. Often, achieving a higher level of passive income requires some active effort immediately following the purchase to optimize operations.
Setting up efficient reporting and communication channels is important, especially if you hire managers or use third-party services like a property manager. Your role becomes focused on strategy, performance monitoring, and addressing major issues, rather than daily tasks. This is how you truly earn passive income from the acquired asset.
Conclusion
Pinpointing the best business to buy for passive income is influenced by your investment capital, personal interests, and the amount of time you realistically plan to commit, even if minimal. Options such as laundromats, self-storage facilities, established digital assets like websites or a YouTube channel, rental property, and even well-placed parking spaces often emerge as strong contenders because their models support systemization and delegation, allowing you to generate passive income.
However, comprehensive investigation and a clear understanding of the specific operation being acquired are indispensable. Achieving great passive income requires more than just purchasing an asset; it involves setting it up for sustained success with minimal daily intervention. Finding the right opportunity requires careful thought and frequently benefits from professional guidance.
Ultimately, the “best” choice aligns with your financial situation, skills, and long-term goals for making money with reduced active effort. Thorough research and due diligence are the foundations for securing a genuinely viable passive income stream through business ownership. This approach helps ensure you make a sound investment and achieve the desired level of passive income.