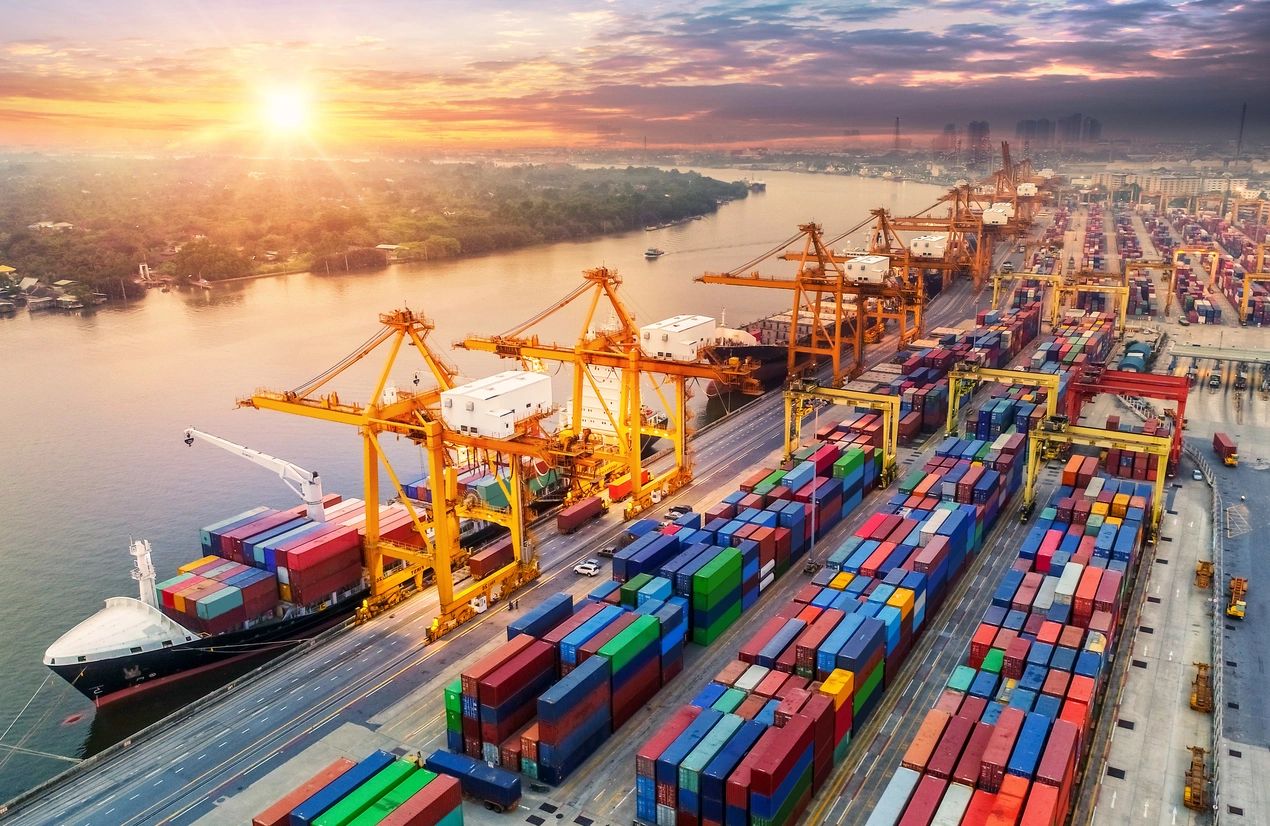
You’re a startup founder, investor, or marketing leader, and you know supply chain management in operations management is critical. But how do you actually make it work *for* you? This isn’t just about logistics—it’s about creating a competitive edge. This post explains supply chain management in operations management, giving you practical know-how to optimize processes, boost customer satisfaction, and drive growth. We’ll cover implementing effective supply chain management (SCM) strategies for success.
🔍 At a Glance: Supply Chain Management in Operations
Featured Summary: Supply Chain Management in operations management serves as the backbone of a business, integrating planning, sourcing, manufacturing, delivery, and returns. By optimizing these interconnected processes, companies can enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve customer satisfaction, thereby gaining a competitive advantage in the market.
Table of Contents:
- What is Supply Chain Management in Operations Management?
- Why is Supply Chain Management Crucial?
- Implementing Effective SCM Strategies
- The Future of SCM
- Conclusion
What is Supply Chain Management in Operations Management?
Supply chain management (SCM) within operations management is the central nervous system of your business. It connects every step, from sourcing raw materials to delivering the final product. Operations management uses supply chains to get everything where it’s needed, when it’s needed.
The Core Components of SCM
Solid SCM hinges on five key phases:
- Planning: Understand customer wants and balance them against production capabilities. Enterprise resource planning (ERP) software can organize complex supply chains, ensuring lead times are accurate for needed manufacturing and that your privacy policy is compliant.
- Sourcing: Strong supplier relationships are essential for reliable supplies and involve sourcing many different raw materials. Negotiate prices with vendors, prioritize flexibility, and ensure good quality for smooth operations.
- Manufacturing: Transforming raw materials into your final product requires examining internal manufacturing processes, including product testing, assembly, and packaging. Watch for wasteful processes and consider Lean, Agile, or Industry 4.0 technologies involving automation, digital transformation, and advanced robotics.
- Delivery: Getting your product to customers affordably and reliably requires order fulfillment strategies to ensure faster delivery. Mitigate risks like weather and supply disruptions with well-defined processes that emphasize quick responses.
- Returns (Reverse Logistics): An excellent return process keeps customers happy and helps improve products by producing goods or offering services using effective SCM to improve product quality across a variety of distribution methods. Returns can signal needed adjustments in design, components, or manufacturing methods. Effective SCM in delivery process emphasizes quick returns and resolutions.
Why is Supply Chain Management Crucial?
Effective supply chain management is crucial for several reasons, especially with operations managers.
Improved Efficiency and Reduced Costs
Streamlining processes reduces costs and lead times while delivering products faster. Companies with effective supply chain management controls often have better profitability. 70% of companies recognize their supply chain’s major impact on customer satisfaction and service.
Better Customer Service
Businesses must prioritize efficient processes to remain competitive. Meeting modern customer demands involves offering flexible options across digital and physical interactions through strategic CRM. Improving efficiency helps supply chain managers deliver improve customer service in all steps of daily operations.
Risk Mitigation
Robust SCM anticipates problems like supply disruptions, negative publicity, lawsuits, or product recalls. Effective chain management controls mean fewer problems overall for the entire chain management team and all chain managers involved.
Boosting Profitability
Forward-thinking businesses utilize monetary policy and fiscal policy while avoiding excess inventory. This frees up capital. Boosting profits demonstrates the supply chain manager’s critical role and all supply chain managers are a major part of this process. Managing the flow of all sourcing involves many factors for many managers and it also directly helps to streamline delivery process overall as well.
Implementing Effective SCM Strategies
Effective operations management is vital for success. Various management models can be applied when streamlining and evaluating strategies. Consider which best meets your goals for the final product:
| Model | Description |
|---|---|
| Lean | Reduces waste in inventory, materials, and processes. |
| Agile | Emphasizes quick responses to changing customer demands and market trends, leading to faster delivery. |
| Six Sigma | Prioritizes data and quality control, minimizing manufacturing flaws using statistical methods. |
| Total Quality Management (TQM) | Focuses on quality in every process, utilizing tools like quality management systems, process planning, and customer feedback. |
| Resilient | Proactively minimizes potential disruptions in internal and external processes. |
| Green | Minimizes environmental impact across all channels, prioritizing ethical and sustainable practices. |
| Digital | Leverages technology like ERP software, AI, and big data for warehouse management, order management, and POS systems, supporting sustainability through streamlined operations and improved order fulfillment across all distribution methods throughout the product lifecycle. |
The Future of SCM
Emerging technologies and sustainability are reshaping supply chains.
Sustainability
Sustainability is not just about being eco-friendly. It also leads to improved profitability through more efficient processes, reduced raw material costs, and less waste. 97% of procurement officers agree that sustainability positively impacts profits.
Technology’s Impact
Technology boosts efficiency across SCM, from warehousing to production planning. Data and AI enhance forecasting, while IoT improves warehouse efficiency, driving digital transformation.
Conclusion
Supply chain management in operations management is a key business strategy for efficient daily operations. Businesses must prioritize optimization, efficiency, and transparency in managing both internal and external supply chain elements.
This includes everything from manufacturing and order fulfillment to customer service and contract negotiations, highlighting the increasing importance of a management major for navigating business administration, quality control, and inventory management while leading teams of operations managers and business operations professionals.
Efficient inventory management requires proper order fulfillment of products with correct lead times from vendors while using enterprise resource planning and effective SCM management.
Whether a startup or a large corporation, the relationship between internal business goals and effective SCM is no longer optional. Embracing SCM leads to increased profits and business success.
Subscribe to my LEAN 360 newsletter to learn more about startup insights.